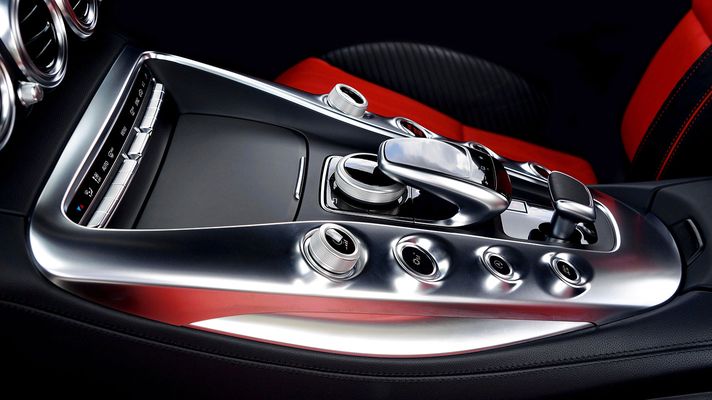
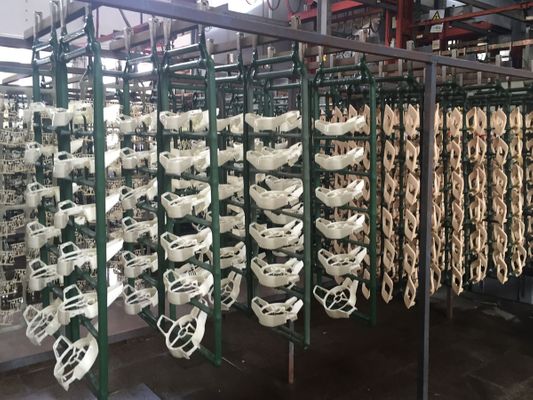
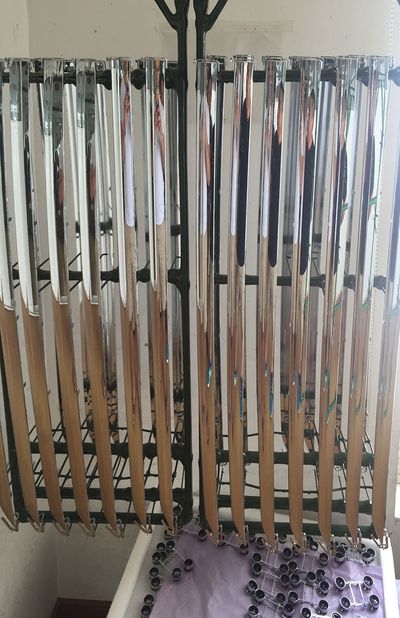
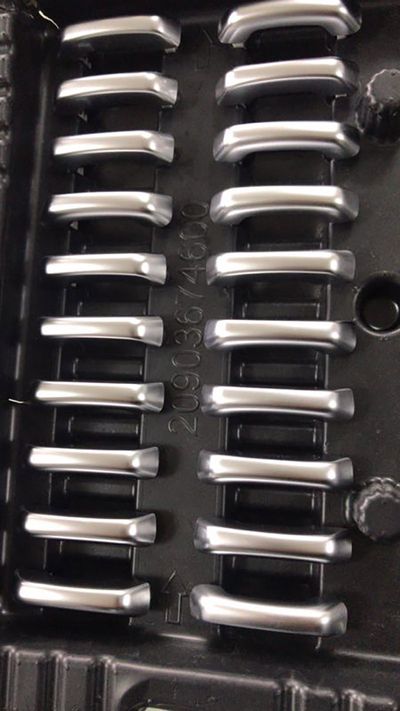
Plating On Plastic
Modern engineered plastics are used in countless industries and applications throughout the world. These materials are popular for many reasons, including their versatility, easy machinability, and excellent surface finishes. However, because plastics are not electrically conductive, they are very difficult to plate with proper adhesion.
Our electroplating projects have been described as having “excellent adhesion and RF performance” by our clients. This is important because many of the applications for plastic plating will be deployed in extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperature or high altitude/low temperature ranges.
Types of Plastic for Electroplating
Polycarbonate
- A strong and durable thermoplastic commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and construction applications.
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
ABS is a low-cost engineering plastic that is easy to machine and fabricate. ABS is an ideal material for structural applications when impact resistance, strength, and stiffness are required. It is widely used for machining pre-production prototypes since it has excellent dimensional stability and is easy to paint and glue.
ABS/PC
(PC+ABS) blends that exhibit an excellent balance of properties, most notably high toughness – even at cold temperatures – rigidity, dimensional stability, excellent creep resistance, low moisture absorption and good heat resistance.
Polysulfone
A thermoplastic polymer known for its transparency, strength, and ability to withstand high heats. Can be seen in many industrial applications where flame retardant plastic is preferred.
PP
Has a greater degree of crystallinity, making PP stiffer and more resistant to creep (the tendency to flow under stress) as compared to polyethylene (PE) PP is resilient and resistant to fatigue; highly resistant to most acids and alkalis; resistant to most organic solvents below 176°F (80°C); can be subjected to steam sterilization.
Nylon
Nylon is one of the most widely used engineering thermoplastics. It offers an excellent combination of mechanical performance and cost. There are many nylon grades available today, the most common being nylon 6/6 and nylon 6. The properties of both nylon products are very similar; and typically, they can be used interchangeably.